|
Bihar is one of the leading states in India that are aggressively taking action for a cleaner environment. The state government, through the Bihar State Pollution Control Board (BSPCB), has undertaken several initiatives over the years to address the issue of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and other pollutants. Specific to the building materials sector, brick-making in Bihar is an important economic activity for many reasons. As per the BSPCB data, brick-making provides employment to around 7.7 million people in Bihar and generates nearly a quarter of the state’s gross domestic product. In addition, bricks sustain the local construction industry. Thus, brick-making units are key rural enterprises in Bihar and a significant contributor to the state’s economy. As of today, burnt clay bricks dominate the landscape of Bihar’s brick-making industry. Over the past two decades and more, Bihar has adopted a slew of measures to enhance the deployment of cleaner technologies for brick production. Recently, BSPCB adopted measures to phase out relatively inefficient brick-making technologies and encourage more efficient equipment in brick production. Currently, there are about 7,757 burnt clay brick kilns and they are manufacturing approximately 22 billion bricks annually (as per the primary data provided by BSPCB). A number of brick-making technologies that are prevalent in the state comprise Fixed Chimney Bull Trench Kilns and Zig Zag Kilns. These kilns use coal as the primary fuel. Also, there are around 453 Fly Ash Brick-making units, which use fly ash primarily from thermal power plants to produce bricks. The use of coal and other sources of non-renewable biomass leads to GHG emissions, contributing to the threats posed by climate change. To reduce the climate change impacts and contribute to the Government of India’s commitments regarding climate change as outlined in the landmark COP26 declaration (MEA, 2021), the Bihar government has also committed to containing its GHG emissions. Being one of the primary emitters of GHGs in the state, the brick-making sector focuses on reducing its GHG emissions and charting a path for achieving carbon neutrality (net zero emissions) (Government of Bihar, 2015). In this regard, Development Alternatives has undertaken a study, with support from Shakti Sustainable Energy Foundation and in association with BSPCB, to do GHG inventorisation of the brick sector of Bihar and develop a roadmap for low-carbon pathways.
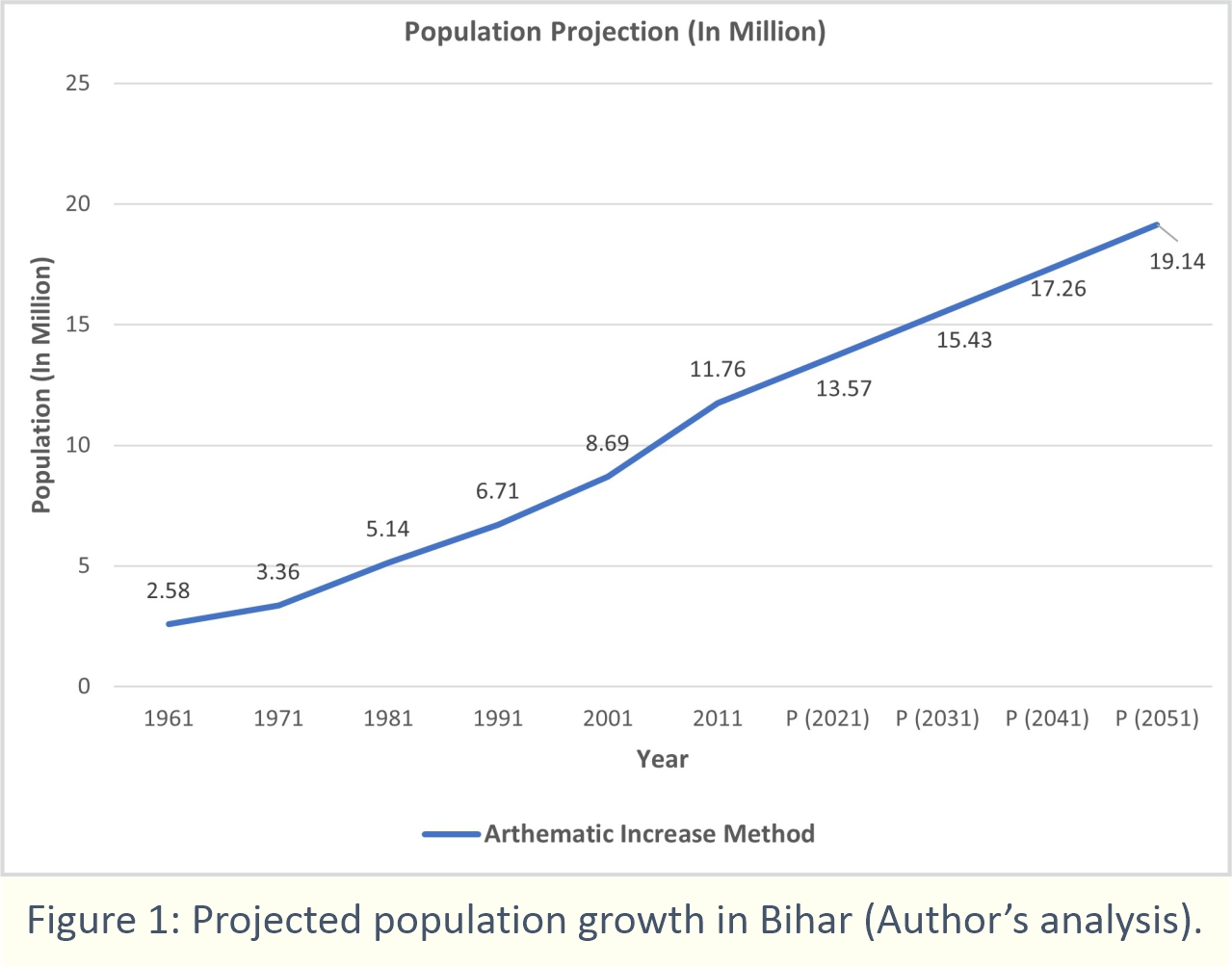
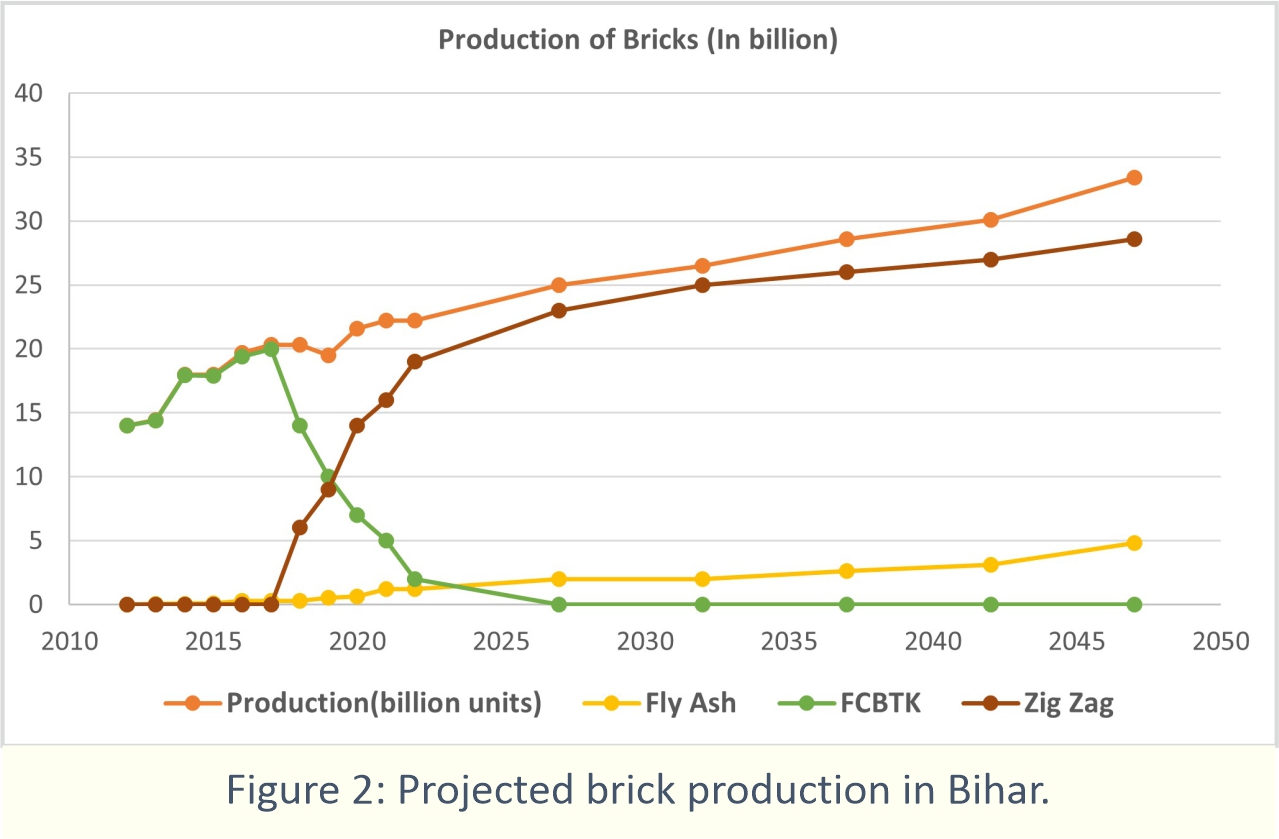
One of the scenarios is shown in Figure 1, wherein the analysis of the population growth in Bihar is given. By this means, one could foresee the development that is to take place within the state, the majority of the built-up area that is yet to come up, and the demand for bricks within the state (projected brick production is shown in Figure 2).
These scenarios were formulated to develop the state’s roadmap to reach carbon neutrality by 2050. Lastly, if emissions from various sectors are not curbed soon, then there is no way the world will be able to limit the temperature increase to 2 degrees Celsius. References DGovernment of Bihar. 2015. Bihar State Action Plan on Climate Change – Building resilience through development. Details available at http://moef.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Bihar-State-Action-Plan-on-Climate-Change-2.pdf, last accessed on 13 Nov, 2021 Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). 2021. National Statement by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi at COP26 Summit in Glasgow. Details available at https://www.mea.gov.in/Speeches-Statements.htm?dtl/34466/National+Statement+by+Prime+Minister+Shri+Narendra+Modi+at+COP26+Summit+in+Glasgow, last accessed on 13 Nov, 2021
Avinash Kumar |
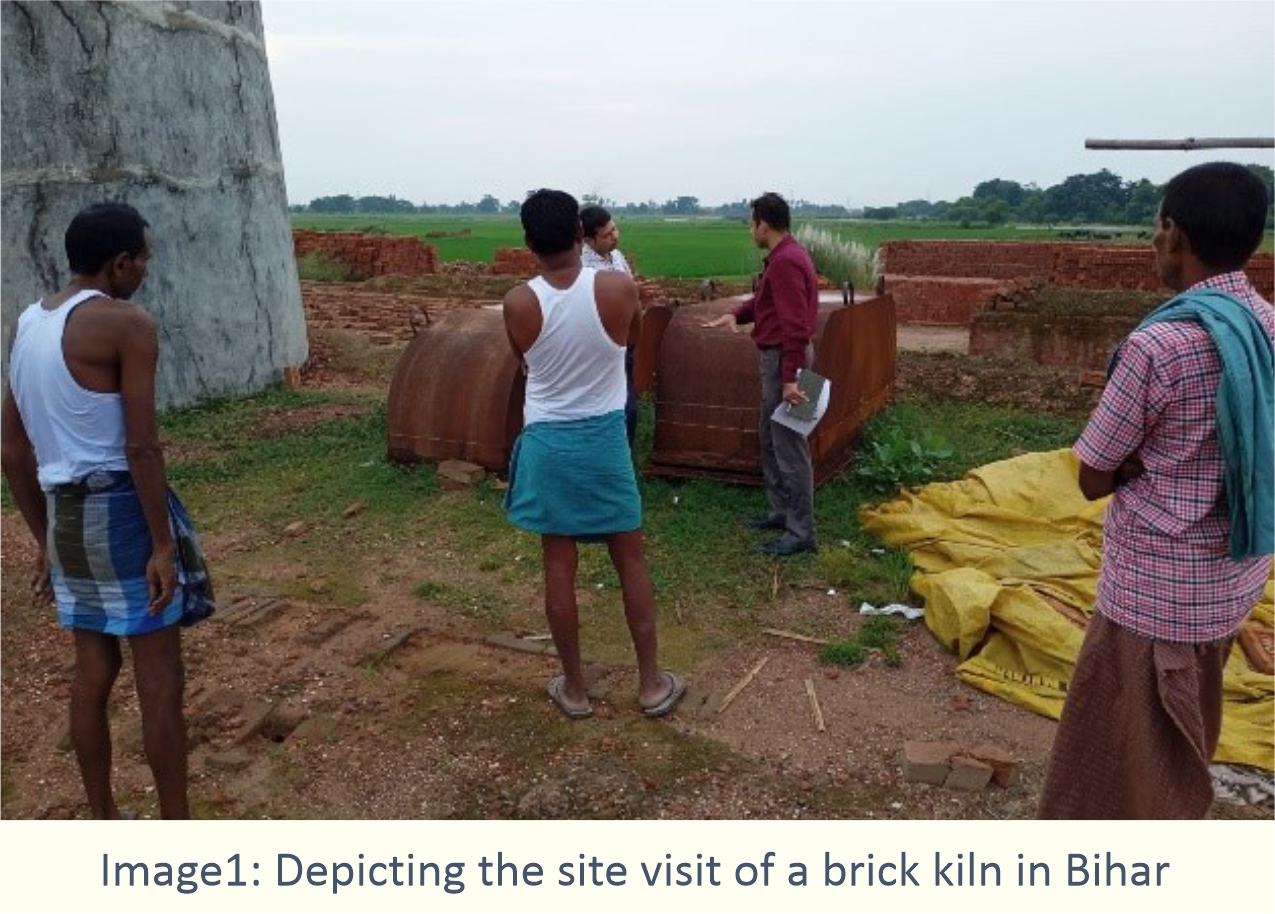 For this, Development Alternatives’ team collected data of numerous
brick kilns within the state from BSPCB. Based on the data and secondary
literature, the team conducted field visits to understand the
manufacturing process and emissions that are released by this informal
sector. The quantification of emissions from the manufacturing process
included studying the kinds of raw materials, fuel, and technology used,
and the final dispatching of bricks to the sellers. By this means, we
were able to conclude that this sector emits approximately 12 million
tonnes of CO2 per annum. Keeping this in mind, we developed various
scenarios, which were applicable to the state, and determine its carbon
emissions.
For this, Development Alternatives’ team collected data of numerous
brick kilns within the state from BSPCB. Based on the data and secondary
literature, the team conducted field visits to understand the
manufacturing process and emissions that are released by this informal
sector. The quantification of emissions from the manufacturing process
included studying the kinds of raw materials, fuel, and technology used,
and the final dispatching of bricks to the sellers. By this means, we
were able to conclude that this sector emits approximately 12 million
tonnes of CO2 per annum. Keeping this in mind, we developed various
scenarios, which were applicable to the state, and determine its carbon
emissions.