|
Achieving Food Security in India A ccording to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), food security exists when all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious
food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and
healthy life. Ensuring food security for all is of great importance for
a country like India that is home to the world’s largest population of
hungry and malnourished people. The lack of proper balanced food can
lead to lower cognitive ability, poor work performance and productivity
losses hampering the potential development of the national economy.
Moreover, increasing population pressures, the reality of climate change
and degradation of natural resources have compounded the need and
complexity to achieve food security like never before. nutritious
food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and
healthy life. Ensuring food security for all is of great importance for
a country like India that is home to the world’s largest population of
hungry and malnourished people. The lack of proper balanced food can
lead to lower cognitive ability, poor work performance and productivity
losses hampering the potential development of the national economy.
Moreover, increasing population pressures, the reality of climate change
and degradation of natural resources have compounded the need and
complexity to achieve food security like never before.
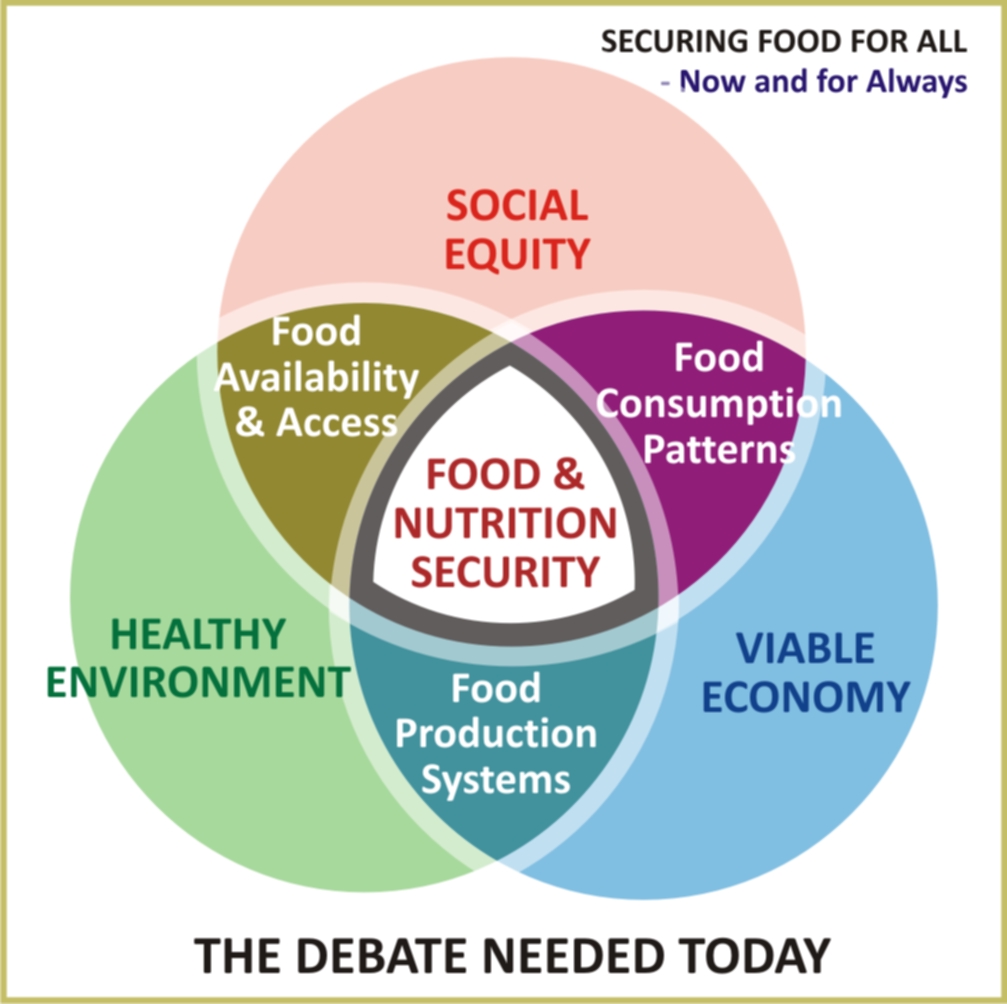
We are now faced by a critical situation where we need to increase agricultural productivity and expand access to food needs of a continually increasing population while enhancing the productive capacity of the natural resource base in a sustainable manner. This must go in hand with efficient use of agro inputs, improved production economics and a concern for the health of the environment. The road for achieving long lasting improvements in food security in India warrants the pursuit of the dual objectives of improving availability and access to food in the short term and improving food production and consumption systems in the medium term. Improving Access and Availability to Food -
Evidence demonstrates that the It is crucial we facilitate development of institutions and design cost-effective safety nets to deliver adequate nutrition to all citizens efficiently and sustainably. We need to gear up distribution systems such that appropriate assistance is provided to the right people at the right time. There is a critical need to create awareness for food and nutrition while creating an environment of stable, affordable prices maintained by a just and regulated market with inbuilt transparency mechanisms. These things would enable universal access to food in the shortest possible time. Beyond this, it is essential that we build capacities of communities such that they have improved purchasing power to access food and other basic needs. Improving Food Production and Consumption The future of food production requires the development of a mix of large and small farms producing a diverse regional food mix demonstrated by various technologies and farming methods that maximise both land and water productivity and farm returns. There is a need for land reforms and incentives for farmers and businesses to increase farm productivity. Crop diversification, improvement in post farm infrastructure and storage systems are all crucial steps that must be adopted. Sustainable management of our natural resources, forests and fisheries is critical for achieving food security. Systems for encouraging production and consumption of both local and green food should be instituted for the desired behaviour change. Conclusion These highlighted aspects are two critical steps to achieve food security. However, these may not be sufficient in the absence of policy coherence and inter-sectoral coordination. Policy instruments and actions across various sectors of the government often distort pricing, lead to suboptimal use of resources, dissuade willingness to invest in farming thus offsetting desired outcomes. We need strong, coherent and coordinated policy responses that address all dimensions of food security and integrate all the three pillars of sustainability – social equity, economic viability and environmental quality - to achieve food for all. q Further Reading: Chitrangna Dewan
|
 poor and marginalised have high fertility rates owing to uncertainty of
survival and hands to earn incomes. However, when life prospects
improve, there is a rapid decline in fertility. A decline in fertility
implies reduced population pressure. Moreover, access to food can
improve productive potential enabling the poor to earn better incomes to
access their own food.
poor and marginalised have high fertility rates owing to uncertainty of
survival and hands to earn incomes. However, when life prospects
improve, there is a rapid decline in fertility. A decline in fertility
implies reduced population pressure. Moreover, access to food can
improve productive potential enabling the poor to earn better incomes to
access their own food.