Towards Sustainable Development
The Brundland Commission in Our Common Future defines sustainable development as “Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their own needs”
ustainable development has
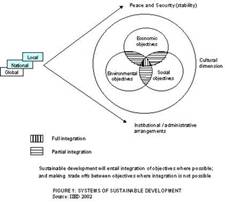
three objectives: economic development; social equit Two major events in the recent past have lucidly articulated the sustainable development challenges and priorities for the global community over the next decade. These include the United Nations Millennium Declaration and the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) – Johannesburg 2002. Johannesburg Plan of Implementation, 2002, called upon countries to take immediate steps to make progress in the formulation and elaboration of National Sustainable Development Strategies and begin their implementation by 2005. As an input to the WSSD, a South Asian Strategy Paper was prepared. It had drawn heavily upon learnings and conclusions from a number of earlier documents prepared for the region. It also had inputs from a group of ‘wise persons’ in the region, multilateral institutions and a series of consultations with governments and civil society. This was followed by a South Asian Priority paper on sustainable development priorities by Development Alternatives.
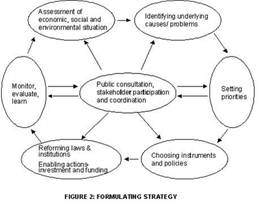
What is National Sustainable Development Strategy (NSDS) and Subregional Sustainable Development Strategy? Development Assistance Committee of OECD (Organisation for Economic Cooporation and Development )has defined NSDS as a coordinated set of participatory and continuously improving process of analysis, debate, capacity-strengthening, planning and investment, which integrates the economic, social and environmental objectives of society and seeks trade-offs where such integration is not possible.
NSDS provides a framework to institutionalize the processes for consultation, negotiation, mediation and consensus building on priority, social, economic and environmental issues. It can empower a country to address complex socio-economic problems such as poverty, population growth and globalization through public participation and improved decision-making. In July 2003, the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation (NORAD) and UNEP Regional Resource Centre for Asia and Pacific (UNEP RRC.AP) started the implementation of the project on National Sustainable Development Strategy and Action Plans (NSDSAP) towards Mainstreaming Sustainable Development in the Decision Making Process. The purpose of the project is to strengthen the capacity of the Asia and the Pacific region and to assist national governments in formulating National Sustainable Development Strategy, Sub-regional Sustainable Development Strategy and Action Plans (NSDSAP) with mainstreaming sustainable development issues in the decision making process. To initiate this, UNEP has identified Development Alternatives as a sub-regional and national Focal Point for South Asia. Under this project a strategy for sustainable development for South Asia is underway, with the priority paper as a guiding document. q Anjna Krishnan kanjana@devalt.org
|
 y,
and environmental conservation. Economic development refers to the well
being of the people and eradication of poverty. Social equity includes:
access to basic needs such as health, education; human security and
rights; gender equity; and distribution of benefits and access to
resources across the society. Environmental conservation concerns itself
with conservation of natural resources and minimizing impacts on
physical and biological resources.
y,
and environmental conservation. Economic development refers to the well
being of the people and eradication of poverty. Social equity includes:
access to basic needs such as health, education; human security and
rights; gender equity; and distribution of benefits and access to
resources across the society. Environmental conservation concerns itself
with conservation of natural resources and minimizing impacts on
physical and biological resources.