|
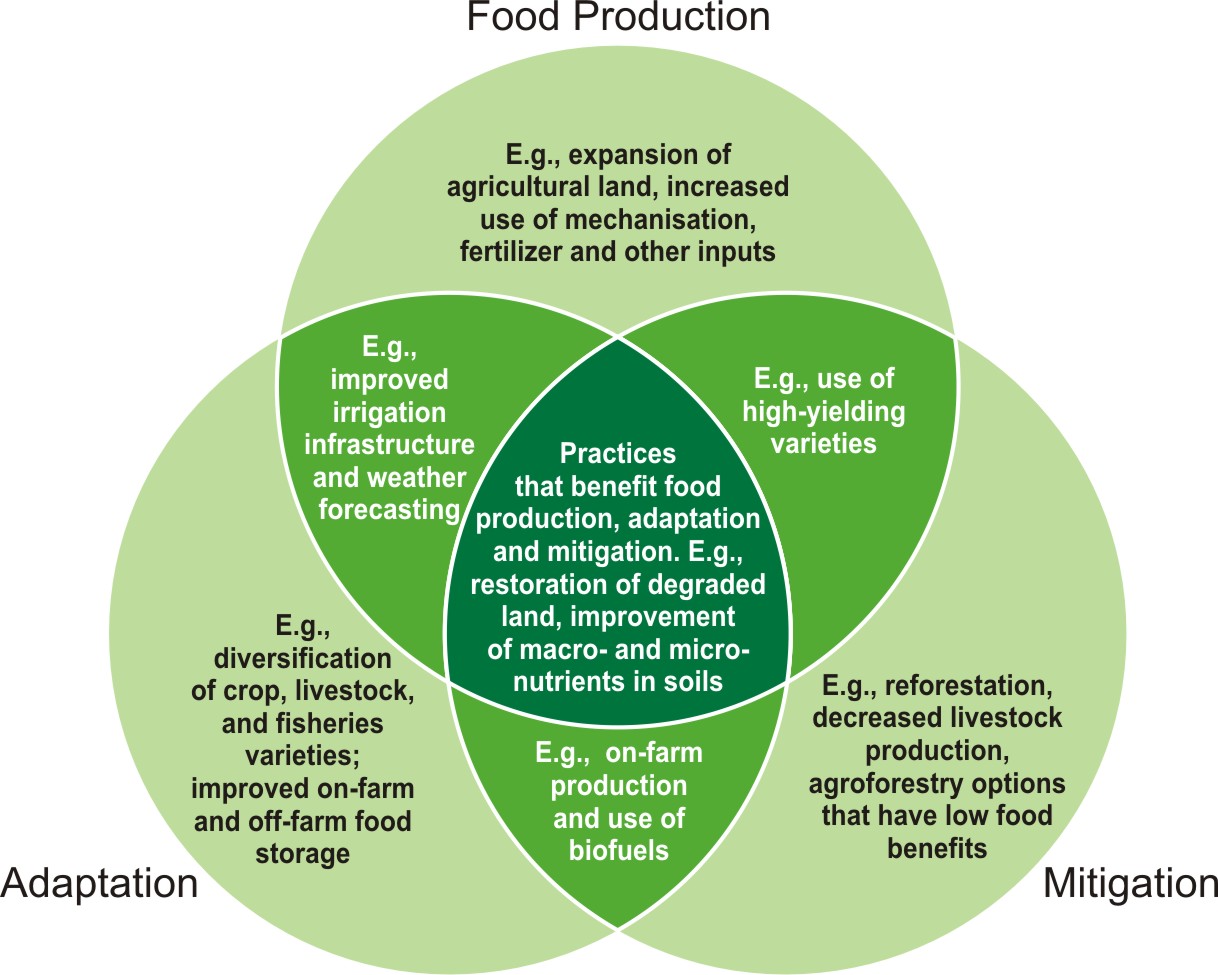
Innovative Approach for I ncreasing temperature and changing rainfall patterns in the coming decades will bring more challenging situations to be faced by agriculture dependent communities followed by food security issues. Forecasts for declining yields are particularly frightening for the developing world and delaying the adaptation mechanism will exacerbate the situation and it will be the poor who will have to pay the heaviest price (WRI 2005).To promote adaptation and building resilience in harmony with nature, FAO is all set to Launch ‘Payment of Environmental Services’ (PES). The activities launched to cope with climate change issues should bring in finance, ecosystems protection as well as poverty reduction in developing countries 1.FAO is promoting Climate Smart
Agriculture (CAS) that sustainably increases productivity, resilience
(adaptation), reduces/removes greenhouse gases (mitigation) while
enhancing the achievement of national food security and development
goals. CAS seeks to support countries in securing the necessary policy, technical and financial conditions to enable increasing sustainable agricultural productivity and incomes, build resilience and capacity of agricultural and food systems to adapt to climate change, and seek opportunities to reduce Green House Gases (GHGs). Implementation of United Nations Reduced Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (UN-REDD Programme) to promote forest-agriculture has been successful in Indonesia 2. UN-REDD Programme brings together technical teams from around the world to develop common approaches, analyses and guidelines on issues such as measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) of carbon emissions and flows, remote sensing, and greenhouse gas inventories. It provides guidance on how best to design and implement REDD+, to ensure that forests continue to provide multiple benefits for livelihoods and biodiversity to societies while storing carbon at the same time. The Programme is also deeply committed to supporting the engagement of Indigenous Peoples and Civil Society organisations in the design and implementation of REDD+ strategies. REDD in now being launched in India as well to protect and conserve forests and reduce GHGs in the environment3.The Global Crop Diversity Trust has announced a major global search to systematically find, gather, catalogue, use, and save the wild relatives of wheat, rice, beans, potato, barley, lentils, chickpea, and other essential food crops. The objective is to help protect global food supplies against the imminent threat of climate change, and strengthen future food security. ICRISAT-TATA-ICAR are partners in combating land degradation and increase productivity in Madhya Pradesh and Eastern Rajasthan". The objective is to minimize land degradation and improve the food security and livelihood opportunities for rural people in rain fed areas of India. The approach involves efficient management and conservation of natural resources through convergence of cost-effective and efficient technologies. These are important as they add great value for integrating adaptation and mitigation with the ultimate goal of reducing the impacts of climate on human livelihoods and thus helping nations to accelerate achievement of UNFCCC targets and MDGs for sustainable development as recommitted in Rio+20. qNeha Gupta 1 http://www.fao.org/docs/up/easypol/868/synergy_building_agric_dev_
climate_mitigation_098en.pdf
|