|
Drip Irrigation
Technology
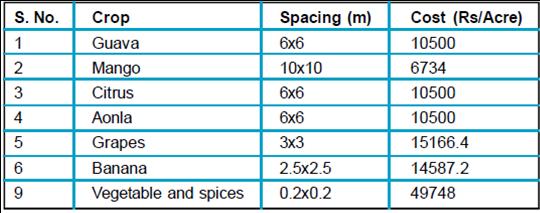
Context Drip irrigation, also known as trickle irrigation or micro-irrigation, is an irrigation method which saves water and fertiliser by allowing water to drip slowly to the roots of the plants, either onto the soil surface or directly into the root zone, through a network of valves, pipes, tubing and emitters. Drip irrigation has been used since ancient times, when buried clay pots were filled with water, which would gradually seep into the grass. Modern drip irrigation was developed in Afghanistan in 1866 when researchers began experimenting with irrigation using clay pipes to create combination irrigation and drainage systems. In 1913, E.B. House at Colorado State University succeeded in applying water to the root zone of plants without raising the water table. A perforated pipe was introduced in Germany in the 1920s and in 1934, O.E. Nobey experimented with irrigating through porous canvas hose at Michigan State University. Drip irrigation is a widely practiced and established method of irrigation in developed countries and is slowly gaining popularity in India. It is most suited for horticultural crops, vegetables etc. and finds applicability in rocky strata terrains like Bundelkhand, where groundwater is scarce. Drip irrigation helps in optimisation of the limited water resources. Modern drip irrigation has arguably become the world's most valued innovation in agriculture since the invention of the impact sprinkler in the 1930s, which offered the first practical alternative to surface irrigation. Advantages and Disadvantages The advantages of drip irrigation are: • Minimised fertilizer/nutrient loss due to localised application and reduced leaching • High water application efficiency. • Leveling of the field not necessary • Ability to irrigate irregular shaped fields • Allows safe use of recycled water. • Moisture within the root zone can be maintained at field capacity • Soil type plays less important role in frequency of irrigation • Minimised soil erosion • Highly uniform distribution of water i.e., controlled by output of each nozzle • Lower labour cost • Variation in supply can be regulated by regulating the valves and drippers • Fertigation can easily be included with minimal waste of fertilizers • Foliage remains dry thus reducing the risk of disease • Usually operated at lower pressure than other types of pressurised irrigation, reducing energy costs The disadvantages of drip irrigation are: • Expense. Initial cost can be more than overhead systems • Waste. The sun can affect the tubes used for drip irrigation, shortening their usable life. Longevity is variable • Clogging can take place if the water is not properly filtered and the equipment not properly maintained • Drip irrigation might be unsatisfactory if herbicides or top dressed fertilizers need sprinkler irrigation for activation • Drip tape causes extra clean-up costs after harvest. You'll need to plan for drip tape winding, disposal, recycling or reuse • Waste of water, time and harvest, if not installed properly. These systems require careful study of all the relevant factors like land topography, soil, water, crop and agro-climatic conditions, and suitability of drip irrigation system and its components • Germination Problems can occur in lighter soils subsurface drip may be unable to wet the soil surface for germination. It requires careful consideration of the installation depth • Most drip systems are designed for high efficiency, meaning little or no leaching fraction. Without sufficient leaching, salts applied with the irrigation water may build up in the root zone, usually at the edge of the wetting pattern. On the other hand, drip irrigation avoids the high capillary potential of traditional surface-applied irrigation, which can draw salt deposits up from deposits below Components The following are the commonly used components of a drip irrigation system arranged in order from the water source. • Pump or pressurised water source • Water Filter(s) - Filtration Systems: Sand Separator like Hydro-Cyclone, Screen filters, Media Filters, Automatic self-cleaning water filters • Fertigation Systems (Venturi injector) and Chemigation Equipment (optional) • Backwash Controller (Backflow Preventer) • Pressure Control Valve (Pressure Regulator) • Main Line (larger diameter Pipe and Pipe Fittings) • Hand-operated, electronic, or hydraulic Control Valves and Safety Valves • Smaller diameter polytube (often referred to as "laterals") • Poly fittings and Accessories (to make connections) • Emitting Devices at plants (ex. Emitter or Drippers, micro spray heads, inline drippers, trickle rings) Government Schemes As a policy to encourage use of such systems, the Government of India under the centrally sponsored scheme for small and marginal farmers to increase irrigation, provides a subsidy to the extent of 50 per cent of the cost of the equipment. The balance amount is made readily available to the farmer through institutional credit. Scheme Requirements Scheme formulation for installation of drip irrigation systems against bank loans require both technical and financial details. The important items that should be included in a scheme for drip irrigation system are given bellow : Introduction This should briefly give the command area, type of plant/tree, required spacing between plants, land scope etc. and general topographic features. Soil The general nature of the soil and its characteristics. Soils have a bearing on the water requirements of crops and setting up the irrigation schedule. Climate and Rainfall The climatic condition and rainfall of the area governs the irrigation requirements of the crops. The evapo - transpiration data is also important. The normal monthly evaporation data as per Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) should necessarily be given, which would greatly help in determining the daily water requirements and irrigation needs in different seasons. Groundwater quality Groundwater quality in the scheme area should be given. Its suitability for irrigation may be indicated in sodium absorption ratio, total dissolved solids etc. Designs of Drip System The designs of the drip system especially the layout, size and length of mains, sub-mains, laterals etc. based on land slope and field plot layout should be given in the scheme. Emitter selection, number of emitters to the plant, water discharge through the emitter and total pumping schedule should be indicated. Well Capacity The source of water should be indicated. If the source of water is a groundwater structure, the diametre, depth and well yield together with HP of the pump set already installed may be given. This is necessary to decide the discharge available from the well and its optimum utilisation. Economics The economics of investment should be given in detail to justify the loan. The scheme should also give details about repayment period, rate of interest, subsidy available etc. Basic Data Information A drip irrigation system requires certain basic data information to plan its layout and ensure trouble-free operation. A format for the required information is given as follows which necessarily should be provided in the scheme. Technical Aspects The design of a drip Irrigation system involves estimation of the following parameters. • Areas to be irrigated, type of plants, their spacing and numbers per hectare • Peak water requirement of a plant per day. For estimation of total water requirement for a given area, the number of emitters required per plant, amount of water discharged per hour through each emitter and the total number of hours water is available should be known/estimated • Design of main and lateral drip Lines. This depends upon friction head loss which in turn is governed by the type of plantation/crop and field configuration • Water required to be pumped from the well. This depends upon hydro geological conditions in the area and water requirement of plants/crop • Horse Power of Pump set, this depends upon discharge and total head including friction losses over which water is to be lifted/pumped • Unit Cost. Given below is a sample of the costs of installing the drip irrigation system for popular horticultural crops Normally a farmer has to arrange for his own down payment as margin money while availing a bank loan. Since subsidy is available for drip irrigation system to all types of farmers, the bank loan is sanctioned in advance, based on the net amount of subsidy. However, often, there is an inordinate delay in sanctions and release of subsidy by government. As a result manufactures/suppliers of drip irrigation system are reluctant to install the system unless full cost is paid. This causes financial difficulties to farmers and adversely affects the progress of installation drip system. q
Dr. Naresh Sharma
|